1. When you have a toothache, you feel pain because _______________.
A. there is a cavity in your tooth
B. tiny bits of food are left between your teeth
C. bacteria digest the food left between your teeth and produce an acid
D. the cavity reaches the nerves and the nerves send a message to the brain
2. Nerve cells tell muscles what to do by using _______________.
A. electrical impulses
B. plasma
C. the spinal cord
D. Vertebra
3. _______________ are specialized cells that are sensitive to stimuli and can turn them into electrical impulses.
A. Effectors
B. Synapses
C. Receptors
4. Any part of the body that produces a response to stimuli.
A. effector
B. neuron
C. receptor
5. Any quick response to stimuli that by passes the brain.
A. reflex action
B. voluntary action
C. knee jerk
6. What are the three (3) main parts of the nervous system?
A. cerebellum, cerebrum, medulla
B. brain, spinal cord, nerves
C. cochlea, nerves, vestibule
7. The cerebellum is the portion of the brain located in the back of the head between the cerebrum and the brain stem. It controls your _______________.
A. balance and coordination
B. breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
C. voluntary movement, speech, hearing, vision, memory, reasoning
8. The cerebrum is the largest part of your brain and is composed of two hemispheres (right and left). It controls your _______________.
A. voluntary movement, speech, hearing, vision, memory, reasoning
B. breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
C. balance and coordination
9. If the left side of your brain is injured then _______________ would be impaired.
A. all bodily functions
B. the left side of the body
C. the right side of the body
10. The outer covering of the brain is called cerebral cortex. It is covered with _______________.
A. axons
B. dendrites
C. nerve cells
D. pons
11. Nerve cells are ball-
A. take in messages from other nerve cells
B. carry messages out of the nerve cell to other nerve cells
C. carry messages in and out of the nerve cell
12. The longer branches extending from a nerve cell are called axons; they _______________.
A. take in messages from other nerve cells
B. carry messages out of the nerve cell to other nerve cells
C. carry messages in and out of the nerve cell
13. The brain stem is the base of the brain that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls your _______________.
A. voluntary movement, speech, hearing, vision, memory, reasoning
B. balance and coordination
C. breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
14. What is the membrane potential when the membrane is hyper polarised.
15. Define the semi-
16. Explain why Hyper-
17. Neurotransmitters are carried in?
18. State three neurotransmitters
19. How does Cocaine affect the brain?
20. Is Venom from the brown snake an antagonist or agonist? Explain why?
21. How are neurotransmitters brought from the cell body to the axon terminals?
22. While at rest the neuron has a high amount of ________ inside and a high amount of ______ outside.
23. Define voltage
24. How do neurotransmitters cross the synapse?
25. Neurotransmitters are synthesised by the _________ and packaged in the ________.
26. During what stage can the neuron not fire?
27. Sodium and potassium are both ________ charged?
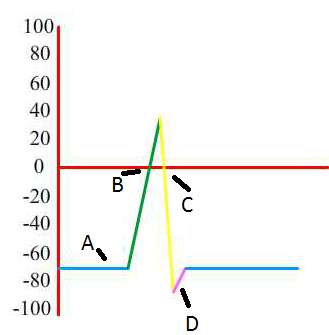
28. What is the resting membrane potential in mV ?
29. Observe the graph to the right.
Name each part and give a brief explanation
as to what is happening to the Sodium and
Potassium at each point.
30. Explain what is meant by the term salatory conduction?
31. What is myelin composed of?